Linter is a static code analysis tool that detects programming and style errors. I use golangci-lint, a fast linter runner, to check my Go code. which is a fast linters runner. It contains an extensive collection of various linters and many configuration options.
Installation
You can install it on Mac with
brew install golangci-lint
Example
// main.go
package main
import (
"fmt"
"os"
)
func main() {
f, _ := os.ReadFile("main.go")
fmt.Printf("%s", string(f))
}
At first glance, this code might look good, but it is not production-ready. You can improve it before committing to the repo.
In this example, you can enable two linters:
- errcheck - which checks for unchecked errors in Go code,
- forbidigo - which prevents committing specific expressions like debug printing.
To do it, you can use the following config:
version: "2"
linters:
enable:
- errcheck
- forbidigo
settings:
errcheck:
# Report about not checking of errors in type assertions: `a := b.(MyStruct)`.
# Such cases aren't reported by default.
# Default: false
check-type-assertions: true
# report about assignment of errors to blank identifier: `num, _ := strconv.Atoi(numStr)`.
# Such cases aren't reported by default.
# Default: false
check-blank: true
You can run the linter with the following command:
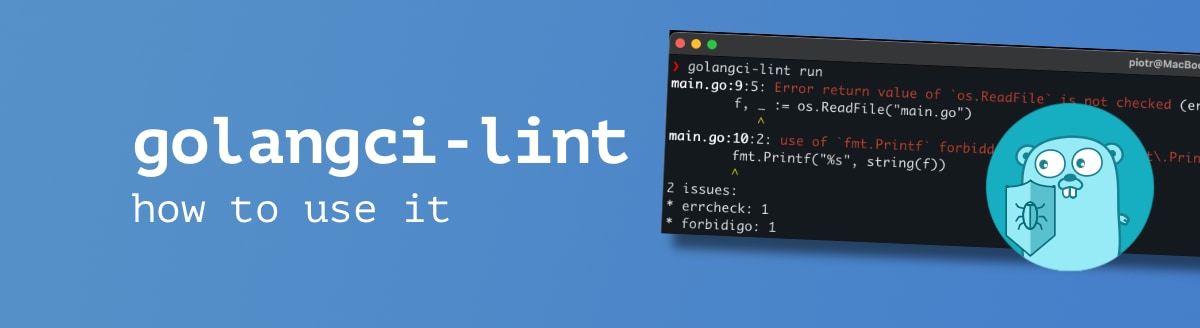
$ golangci-lint run
main.go:9:5: Error return value of `os.ReadFile` is not checked (errcheck)
f, _ := os.ReadFile("main.go")
^
main.go:10:2: use of `fmt.Printf` forbidden by pattern `^(fmt\.Print(|f|ln)|print|println)$` (forbidigo)
fmt.Printf("%s", string(f))
^
2 issues:
* errcheck: 1
* forbidigo: 1
You have two error messages, so let’s fix them.
Fixing error checking
To address the first problem, let’s check the return value and log the error if it exists.
package main
import (
"fmt"
"log"
"os"
)
func main() {
f, err := os.ReadFile("main.go")
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
fmt.Printf("%s", string(f))
}
Let’s verify with the linter.
$ golangci-lint run
main.go:14:2: use of `fmt.Printf` forbidden by pattern `^(fmt\.Print(|f|ln)|print|println)$` (forbidigo)
fmt.Printf("%s", string(f))
^
1 issues:
* forbidigo: 1
$ echo $?
1
Fixing fmt.Printf
To fix the second issue, you can either remove the fmt.Print before committing to the repo or changing it to the log statement. Let’s choose the second option here:
package main
import (
"log"
"os"
)
func main() {
f, err := os.ReadFile("main.go")
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
log.Printf("main.go: %s", string(f))
}
The last linter run returns no error and exit code 0.
$ golangci-lint run
0 issues.
$ echo $?
0
Choosing right linters
The list of linters and the number of configuration options can be overwhelming. I recommend reading about them, checking other configs, and adapting to your needs. Example configs:
- https://gist.github.com/maratori/47a4d00457a92aa426dbd48a18776322
- https://gist.github.com/cristaloleg/f1610a9ca73ac420cda170fadd21b944 blog post
Linter workflow integration
You can integrate linters into the workflow, so running the command manually in the terminal after every code change is unnecessary. golangci-lint integrates with the most popular editors like:
- Goland
- VSCode
- Vim
It can be added as pre-commit hook.
As well as Continous Integration step: CI integration